The same way we approach security with our online existence , we do with our Moodle and Totara sites. In this post, we discuss the difference between an 'http' and 'https' site and what a Moodle / Totara site administrator can do in relation to password policy settings.
1 What is an SSL certificate, what's the difference between 'http' and 'https' sites and why do I need an SSL certificate for my e-Learning site?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between your site and a user's web browser. Although SSL has now been replaced by TLS (Transport Layer Security) this is commonly referred to as “SSL” and we do so here. However, our hosting platform uses TLS encryption.
SSL allows data (such as login details) to be transmitted securely. Without SSL, data sent between browsers and web servers is in plain text.
From a user's point of view, with an SSL certificate in place, the URL of your site will commence with 'https' (as opposed to 'http') and, depending on your web browser, you and your visitors will see the familiar padlock icon.
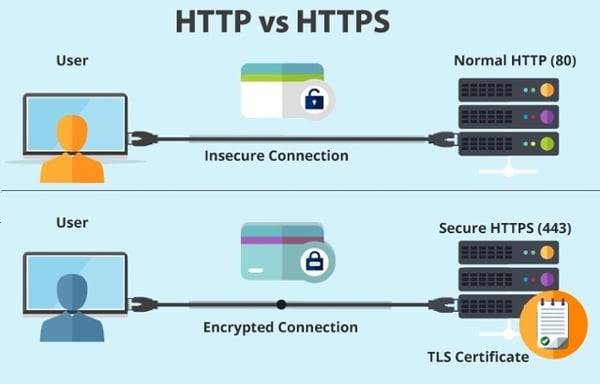
While it's not essential, we strongly recommend that all Moodle and Totara sites have an SSL certificate installed to ensure the security of you and your user's data when moving between your site and your learning management site. This is especially important when authenticating with other systems.
While we install SSL certificates as standard in our hosting plans, if you prefer to host your site in-house, we can install and manage the certificate for you.
2 There is quite a bit that Moodle and Totara administrators can do for passwords on their site
- You can fine-tune the password policy by defining how many characters it should be, how many digits, lowercase or uppercase letters, how many non-alphanumeric characters there should be.
- Define how many times a user has to change their password before they are allowed to reuse a previous one.
- Force the user to log-out after changing a password
- Define a maximum time to validate a password reset request
- Define a maximum number of failed login attempts before the account is locked.